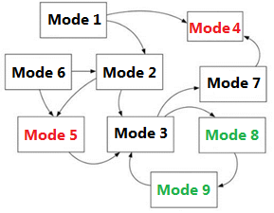
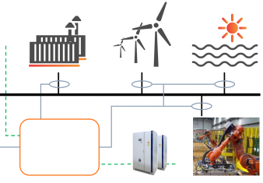
| Many of the dynamical systems can be mathematically described in terms of continuous-valued variables. However, with the increasing complexity of newer engineering applications, it is no longer sufficient to rely on models that are expressed in terms of only continuous variables. In many of the systems, the model variables are discrete-valued for example in logical computing elements or in devices with ON/OFF or multi-mode states. Complexity of a system e.g. due to composition of subsystems with different types of variables can result in a dynamical system with a hybrid set of continuous/discrete state variables which is briefly denoted as a hybrid system. |
|  |  |


